Definition
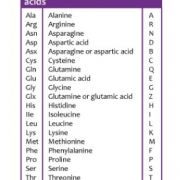
The chemical building blocks of which proteins are made. There are 20 different types of amino acids which can combine in various forms to produce the many different proteins in our bodies.
Use in clinical context
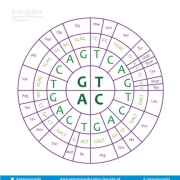
The order of amino acids in a protein affects its structure and function. This order is encoded by the DNA in the corresponding gene. Some changes to the DNA sequence can change the encoded amino acid and therefore the final protein. By identifying a change in the DNA, it is possible to establish if this will change the encoded amino acid and have a functional impact. This information can be used to establish the cause of a condition and if a particular treatment is appropriate.