Definition
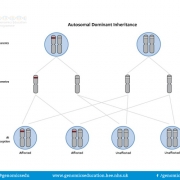
When two copies of a gene are present a dominant allele will result in the associated phenotype being expressed even when the dominant allele is only present on one copy of the chromosome.
Use in clinical context
Individuals usually have two copies of each gene, with the exception of genes on the sex chromosomes in males. Both copies of the gene can contribute to an individual’s phenotype. Dominant alleles will produce the phenotype associated with them, even in the presence of another allele.
Related terms
Allele | Chromosome | Dominant phenotype | Gene | Heterozygous | Phenotype | Recessive allele | Sex chromosome