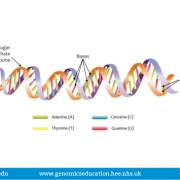
Definition
The molecular structure formed by two strands of DNA.
Use in clinical context
The structure of DNA is a double helix due to the orientation and arrangement of the nucleotides that make up each strand. The double-stranded nature of DNA also benefits replication, where each single strand can act as a template to build two new complementary ones. In the vast majority of naturally occurring situations the DNA structure is a right-handed helix, spiralling anticlockwise if looked at from the end.