Use in clinical context
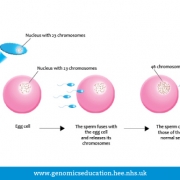
Eggs are formed through the process of meiosis. Each egg is haploid, it contains a single copy of each chromosome with the sex chromosome always an X chromosome. In addition, eggs are also the source of all the mitochondrial DNA found in a fertilised cell. Eggs contain the mother’s genetic contribution to any offspring. An egg and sperm combine during fertilisation to form a diploid cell that goes on to become a complete individual.
Related terms
Cell | Chromosome | Fertilisation | Gamete | Haploid | Meiosis | Mitochondria | Sperm