Definition
When there are multiple genetically different populations of cells within one individual.
Use in clinical context
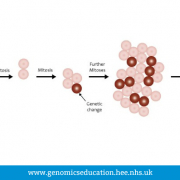
New variants can arise in cells at any point during a person’s lifetime. If this occurs in the early stages of development, the variant will be present in a large number of cells within the body. This can result in multiple presentations as the cells give rise to different parts of the body. Conversely, a variant may occur later in life giving rise to a localised population of cells with the change that only affects a single tissue or part of a single tissue. Some cancers are the result of new variants and are an example of mosaicism affecting only a part of the body.