Definition
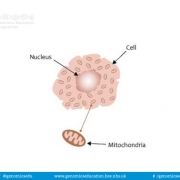
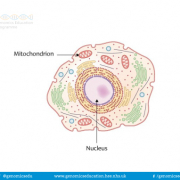
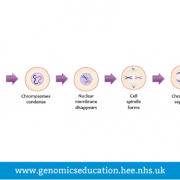
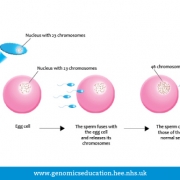
Largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell and the place where the majority of DNA is found.
Use in clinical context
Most DNA is contained within the nucleus of the cell, with the exception of DNA found in the mitochondria. The nucleus prevents chromosomal DNA from interacting directly with other organelles, therefore genes are transcribed into RNA to be transported out of the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are produced.
Typically, cells only contain one nucleus but there are exceptions. Some cells have multiple nuclei – they are multinucleated. Sometimes this occurs in healthy tissue such as muscle and liver, but this can be a sign of disease, for example cancerous cells often have multiple nuclei. Other cells, including mature red blood cells, do not contain a nucleus.
Related terms
Cell | Cell division | Chromosome | Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) | Eukaryote | Mitochondria | Organelle | Protein | Ribose