Definition
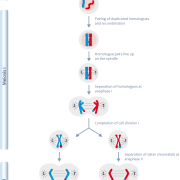
The spindle, a complex of tube-like protein structures, extends from one side of the cell to the other during cell division. Chromosomes attach to the spindle via their centromeres and are drawn to opposite ends of the cell as it divides.
Use in clinical context
The spindle is important in ensuring that following cell division the resulting daughter cells have the correct number of chromosomes. Improper separation of the chromosomes – if the spindle does not form properly or if the chromosomes do not attach correctly – leads to aneuploidy in the daughter cells.
Related terms
Aneuploidy | Cell | Cell division | Chromosome | Daughter cells | Protein